Mini Circuit Breakers protect panels and circuits while allowing fast, modular, space-saving maintenance.
Need Miniature Breakers?
Get Mini Breaker Quote- What’s an Industrial Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)?
- Miniature Breaker Code Compliance and SCCR Safety
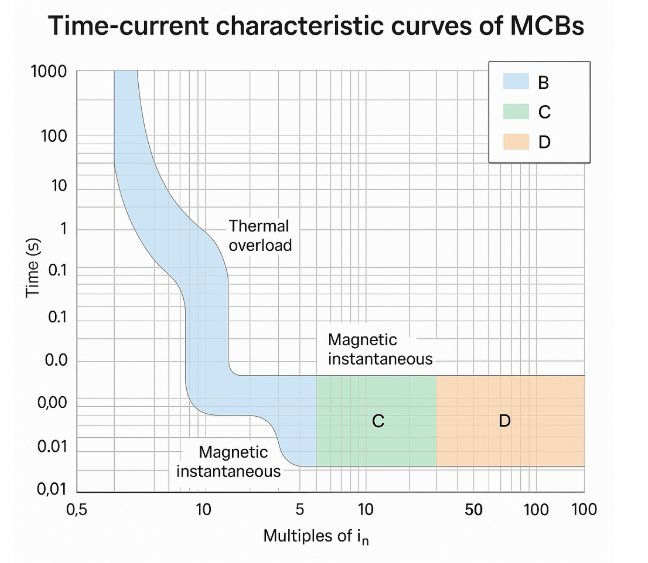
- How They Trip: MCB Trip Curve Values
- Mounting a DIN Rail Miniature Circuit Breaker
- Sizing Industrial Miniature Circuit Breakers
- Panel Efficiency with a DIN Rail Breaker
- MCB Essentials: Trip Curves, DIN-Rail Standardization
- Glossary Terms to Know
- Mini Circuit Breaker FAQ

| Part Number | Description |
|---|---|
| FAZ-B1/1-NA | MCB, B curve, 1 A, 1-pole, up to 277 VAC (UL 489), DIN-rail |
| FAZ-B6/1-NA | MCB, B curve, 6 A, 1-pole, up to 277 VAC (UL 489), DIN-rail |
| FAZ-B10/1-NA | MCB, B curve, 10 A, 1-pole, up to 277 VAC (UL 489), DIN-rail |
| FAZ-B20/1-NA | MCB, B curve, 20 A, 1-pole, up to 277 VAC (UL 489), DIN-rail |
| FAZ-B32/1-NA | MCB, B curve, 32 A, 1-pole, up to 277 VAC (UL 489), DIN-rail |
| FAZ-C6/1-NA | MCB, C curve, 6 A, 1-pole, up to 277 VAC (UL 489), DIN-rail |
| FAZ-C10/1-NA | MCB, C curve, 10 A, 1-pole, up to 277 VAC (UL 489), DIN-rail |
| FAZ-C16/1-NA | MCB, C curve, 16 A, 1-pole, up to 277 VAC (UL 489), DIN-rail |
| FAZ-C20/2-NA | MCB, C curve, 20 A, 2-pole, up to 480Y/277 VAC (UL 489), DIN-rail |
| FAZ-C32/3-NA | MCB, C curve, 32 A, 3-pole, up to 480Y/277 VAC (UL 489), DIN-rail |
| FAZ-D6/1-NA | MCB, D curve, 6 A, 1-pole, up to 277 VAC (UL 489), DIN-rail |
| FAZ-D10/1-NA | MCB, D curve, 10 A, 1-pole, up to 277 VAC (UL 489), DIN-rail |
| FAZ-D16/3-NA | MCB, D curve, 16 A, 3-pole, up to 480Y/277 VAC (UL 489), DIN-rail |
Visit Relectric Eaton FAZ Mini Breaker Product Page

Glossary Terms to Know
- Branch Circuit — The wiring and devices downstream of the final overcurrent protective device feeding loads.
- Interrupting Capacity (SCCR) — The maximum fault current a device can safely interrupt.
- Inrush Current — A short surge of current when equipment starts, often driving curve selection.
- Selectivity (Coordination) — So that only the nearest protective device trips for a fault.
- Derating — Reducing a device’s nominal rating to account for temperature, grouping, or altitude.
- Auxiliary Contact — Low-level signaling contact indicating breaker status.
- Shunt Trip — Coil that opens the breaker remotely for safety interlocks or emergency stops.
Mini Circuit Breaker FAQ
Pick UL 489 for branch-circuit protection of conductors; UL 1077 is only for supplementary equipment protection downstream of a compliant OCPD.
Start with C for typical motors; use D when you expect high inrush or hard starts. Validate with motor data.
Physically, yes, but terminal geometry, accessories, and ratings differ. Keep families consistent for documentation and service.
Obtain available fault current at the panel, then select an MCB with equal or higher interrupting capacity, considering upstream protection.
Aux contacts help with status indication; shunt trips integrate with safety circuits. Add only what your control logic requires.
Misapplied curves, undersized conductors, loose terminations, or unexpected inrush. Measure inrush and retorque connections.
Not generally. Minis excel in control panels and lighter branch loads. Use MCCBs where higher currents or advanced protection functions are required.
Looking for Circuit Breaker Troubleshooting Tips and Advice?
Common Circuit Breaker Problems
How to Replace a Circuit Breaker
How to Test a Circuit Breaker
Installing Circuit Breakers
Types of Circuit Breakers
